Blog Last Updated on 2 years ago by
When it comes to agriculture, soil is one of the most critical factors that determine the success of crops. Each region has its unique soil composition, which depends on various factors such as climate, topography, vegetation, and geology.
Andhra Pradesh, a state located in southeastern India, is known for its diverse agriculture sector. However, the state’s agriculture productivity is heavily influenced by the different types of soils In Andhra Pradesh found in the region. Some may argue that soil composition may not be a significant factor in agriculture productivity, but a closer look at Andhra Pradesh’s agriculture sector will challenge that notion.
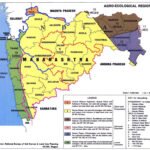
The state of Andhra Pradesh has a rich soil diversity, with each region having its unique soil type. From alluvial soils to laterite soils, each type of soil has its characteristics and properties that determine the crops that can be grown.
However, it is essential to note that the impact of soil types on agriculture productivity in Andhra Pradesh is significant. Understanding the different types of soils in the region, their properties, and how they affect agriculture is crucial in developing effective soil management practices that will improve crop yield and boost the sector’s productivity.
Key Takeaways
- Alluvial, black cotton, red, laterite, coastal, and saline soils are the main soil types in Andhra Pradesh, each with different properties and suitability for various crops.
- Understanding soil types is important to effectively manage soil health and improve crop yield through techniques such as crop rotation, intercropping, and use of organic fertilizers.
- Soil conservation techniques, including contour farming, terracing, and mulching, can help combat soil erosion, while efficient irrigation practices like drip irrigation can mitigate water scarcity.
- Precision agriculture techniques and developing drought-resistant crops through sustainable practices can help mitigate the challenges of climate change, declining soil fertility, and water scarcity in the agriculture sector.
Alluvial Soils in Andhra Pradesh
Alluvial soils, which are formed by the deposition of sediment carried by rivers, are found in abundance in Andhra Pradesh, such as the Krishna and Godavari river basins, where they support rice cultivation. These soils are made up of a mixture of sand, clay, and silt, which varies in proportion depending on the location of the soil. Alluvial soils are mainly found in the delta regions of the rivers, where they are deposited as river silt.
The characteristics of alluvial soils in Andhra Pradesh are unique, making them suitable for various agricultural practices. They are rich in organic matter, have good water retention capacity, and are easy to till. These soils also have a high fertility level and are suitable for growing crops such as rice, sugarcane, and pulses. The agricultural productivity of alluvial soils in Andhra Pradesh is high, making it one of the most productive regions in India.
Moving forward, black cotton soils in Andhra Pradesh are another important type of soil that affects agricultural productivity in the region. These soils have their own unique characteristics that differ from alluvial soils.
Black Cotton Soils in Andhra Pradesh
Black Cotton Soils, also known as regur soils, are highly productive and sought after by farmers due to their unique properties and ability to retain moisture, making them ideal for cultivating crops in dry regions. These soils are characterized by their dark color, deep cracks, and high clay content. They are found in the Deccan plateau region of India, including Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Maharashtra.
In Andhra Pradesh, black cotton soils are distributed in the districts of Anantapur, Kadapa, Kurnool, and Chittoor. The properties of black cotton soils make them suitable for a variety of agricultural practices, including the cultivation of cotton, groundnut, sugarcane, and maize. These crops thrive in the high water-holding capacity of the soil, which helps to mitigate the impact of droughts.
However, the high clay content of black cotton soils can pose challenges for farmers, as it can lead to poor drainage and soil erosion. Additionally, these soils are prone to cracking during the dry season, which can make it difficult for crops to take root.
Overall, black cotton soils play a vital role in the agricultural economy of Andhra Pradesh, providing farmers with the means to cultivate crops in dry regions. However, the challenges posed by the unique properties of these soils require careful management and conservation efforts to ensure their continued productivity.
In the following section, we will explore the distribution and properties of another important soil type in Andhra Pradesh, red soils.
Red Soils in Andhra Pradesh
One of the major soil types found in the Deccan plateau region of India, characterized by its reddish color and low fertility, is commonly known as red soil. These soils have a high iron content due to the presence of hematite, which gives them their distinct red coloration. They are also characterized by their sandy texture and low water-holding capacity, making them prone to erosion and leaching.
Despite their low fertility, red soils are suitable for growing a variety of crops, including cotton, groundnuts, and pulses. However, they require careful management to maintain their productivity. This can be achieved through practices such as crop rotation, intercropping, and the use of organic fertilizers. In addition, irrigation is essential for successful cultivation of these soils, as they are prone to drought.
In summary, red soils are a common soil type found in the Deccan plateau region of India. They are characterized by their sandy texture, low water-holding capacity, and low fertility. Despite these limitations, they can be managed to produce a variety of crops, including cotton, groundnuts, and pulses.
In the next section, we will discuss another important soil type found in Andhra Pradesh – laterite soils.
Laterite Soils in Andhra Pradesh
Laterite soils, formed by intense chemical weathering of rocks in tropical regions, are a common soil type in the Deccan plateau region of India, including Andhra Pradesh. These soils are characterized by their high iron and aluminum content, which gives them a reddish-brown color. They are also highly porous, which means that they have a low water-holding capacity and require frequent irrigation.
In Andhra Pradesh, laterite soils cover a large area, especially in the districts of Srikakulam, Vizianagaram, Visakhapatnam, East Godavari, and West Godavari. Due to their low fertility, farming practices on laterite soils require careful management. Farmers typically use fertilizers and organic amendments to improve soil fertility and crop yields. In addition, crop rotation and intercropping are also commonly used to maintain soil health.
Overall, the cultivation of crops on laterite soils in Andhra Pradesh requires careful management and a thorough understanding of their properties. Farmers must take into consideration factors such as soil fertility, moisture retention, and crop selection to ensure that their crops thrive.
In the next section, we will discuss another important soil type in Andhra Pradesh – coastal soils.
Coastal Soils in Andhra Pradesh
Coastal areas in this region of India are characterized by a unique soil type with distinct properties. Coastal soils in Andhra Pradesh are formed due to the deposition of sediments by rivers, waves, and tides. These soils are generally sandy, saline, and have a high water table.
Here are some key characteristics of Coastal Soils in Andhra Pradesh:
- High salt content: Coastal soils in Andhra Pradesh have a high salt content due to their proximity to the sea. This makes them unsuitable for most crops, with the exception of salt-tolerant varieties.
- Low organic matter: Coastal soils are generally low in organic matter, as the high salt content inhibits the growth of vegetation.
- Vulnerability to coastal erosion: Coastal erosion is a major problem in Andhra Pradesh, and the sandy nature of coastal soils makes them particularly vulnerable to erosion.
- Soil pollution: Coastal soils are also vulnerable to pollution from industrial and agricultural activities, which can have a negative impact on the environment and human health.
In summary, Coastal soils in Andhra Pradesh are unique and have distinct properties that make them unsuitable for most crops. Their vulnerability to erosion and pollution poses a significant challenge for sustainable development in the region.
The next section will focus on Saline Soils in Andhra Pradesh.
Saline Soils in Andhra Pradesh
Saline conditions in the soil of Andhra Pradesh pose serious challenges to agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability. The high concentration of salts in the soil is a result of factors such as high evaporation rates and low rainfall. These conditions render the soil unsuitable for most crops, leading to reduced yields and economic losses for farmers.
Saline soil management is crucial for sustaining agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability in the region. Some crop adaptation strategies that have been successful in managing saline soils include using salt-tolerant crops and soil amendments such as gypsum and organic matter. These strategies help to improve soil structure, reduce soil salinity, and increase water-holding capacity.
Effective management of saline soils requires a comprehensive understanding of the soil characteristics and properties. Soil texture, pH, electrical conductivity, and water-holding capacity are key factors that influence the salinity levels in the soil. By understanding these factors, farmers and researchers can develop effective strategies for managing saline soils and enhancing agricultural productivity in Andhra Pradesh.
Soil Characteristics and Properties
Understanding the various soil characteristics and properties is crucial in developing effective strategies for enhancing agricultural productivity and sustainability in Andhra Pradesh. The state’s soil has an average organic matter content of only 0.5%, which means that farmers face significant challenges in maintaining soil fertility. However, soil fertility is not the only factor that determines the productivity of agricultural land. Other soil characteristics such as texture, nutrient composition, and water-holding capacity also play a significant role.
- Texture: The texture of soil refers to the size distribution of its mineral particles. Andhra Pradesh has sandy loam, red sandy loam, and laterite soils. Sandy soils are well-drained and easy to work with, but they have low water-holding capacity and are prone to erosion. Clay soils, on the other hand, have high water-holding capacity but are difficult to work with.
- Nutrient composition: The nutrient composition of soil is critical for plant growth and development. Andhra Pradesh’s soils are generally deficient in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are essential for plant growth, and their absence can lead to stunted growth and poor yields. Farmers in the state must apply fertilizers to compensate for nutrient deficiencies and maintain the soil’s fertility.
- Water-holding capacity: The water-holding capacity of soil is its ability to retain water for use by plants. Andhra Pradesh has a predominantly dry climate, which means that water availability is a critical factor in agricultural productivity. Sandy soils have low water-holding capacity and require frequent irrigation, while clay soils have high water-holding capacity but can become waterlogged if over-irrigated.
In conclusion, soil characteristics such as texture, nutrient composition, and water-holding capacity have a significant impact on agricultural productivity in Andhra Pradesh. Soil fertility is only one aspect of soil quality, and farmers must consider multiple factors when developing strategies to enhance agricultural productivity and sustainability. The impact of soil types on agriculture in Andhra Pradesh will be further explored in the next section.
Impact of Soil Types on Agriculture in Andhra Pradesh
The productivity and sustainability of agriculture in Andhra Pradesh are significantly influenced by the types of soil present in the region. The state has a diverse range of soils, including black, red, alluvial, and laterite soils. Each type of soil has its distinct properties and characteristics that impact crop growth and yield.
For example, black soils are rich in nutrients and organic matter, making them suitable for cotton and sugarcane cultivation. In contrast, red soils have low fertility levels and require intensive soil management practices to improve crop productivity.
One of the significant challenges faced by farmers in Andhra Pradesh is soil erosion, which is the loss of topsoil due to water or wind. Soil erosion negatively impacts soil fertility and crop productivity, leading to reduced yields and income. To combat soil erosion, farmers in the state practice soil conservation techniques such as contour farming, terracing, and mulching. Additionally, the use of cover crops and crop rotation helps to improve soil health and prevent erosion.
Soil fertility management techniques are critical for ensuring sustainable agriculture in Andhra Pradesh. These techniques involve using organic and inorganic fertilizers to replenish soil nutrients and maintain soil fertility levels. Farmers in the state also use soil testing to determine the nutrient levels in the soil and make informed decisions about fertilizer application. The state government provides subsidies and incentives to farmers to encourage the adoption of soil fertility management practices, ultimately leading to increased crop productivity and improved livelihoods for farmers.
Transitioning into the subsequent section on soil management practices, it is essential to note that farmers in Andhra Pradesh implement a range of techniques to manage soil health and fertility. By adopting appropriate soil management practices, farmers can improve soil fertility, prevent erosion, and increase crop yields.
Soil Management Practices in Andhra Pradesh
Farmers in this region employ a variety of effective measures to maintain soil fertility and prevent erosion, such as using cover crops, crop rotation, and applying organic and inorganic fertilizers. Efficient irrigation practices are also used to ensure that water is used effectively and not wasted. This is especially important in areas where water is scarce or seasonal, such as in the Rayalaseema region.
Crop rotation involves the practice of alternating different crops on the same land to maintain soil fertility and prevent the buildup of pests and diseases. This is particularly important in Andhra Pradesh, where the same crops are often grown year after year, leading to soil depletion and reduced yields. By rotating crops, farmers can maintain soil health and maximize their yields.
Efficient irrigation practices are also critical in Andhra Pradesh, where water resources are limited. Drip irrigation, for example, allows farmers to apply water directly to the roots of plants, reducing water waste and increasing yields. In addition, farmers are increasingly using precision irrigation techniques, which involve monitoring soil moisture levels and applying water only when necessary. These practices not only conserve water but also increase crop yields and reduce the risk of crop failure.
Looking ahead, Andhra Pradesh’s agriculture sector faces several challenges, including climate change, declining soil fertility, and water scarcity. However, by adopting innovative practices such as efficient irrigation and crop rotation, farmers can continue to maintain soil health and increase their yields. With the right policies and investments, the state’s agriculture sector can thrive in the years to come.
Future Prospects and Challenges for Andhra Pradesh’s Agriculture
The sustainability of Andhra Pradesh’s agriculture sector is facing multiple challenges, including soil fertility decline, water scarcity, and climate change. In order to maintain the productivity and viability of agriculture in the region, innovative solutions and investments are necessary.
One potential solution is the adoption of precision agriculture techniques, which use data and technology to optimize crop yields while minimizing resource use.
Another area where innovation is necessary is in the development of drought-resistant crops. With water scarcity becoming an increasingly pressing concern in Andhra Pradesh, crops that require less water or can tolerate drought conditions will be essential for maintaining agricultural productivity in the region. Additionally, improving soil health through the use of organic fertilizers and other sustainable practices can also help to mitigate soil fertility decline and ensure long-term agricultural productivity.
Despite these challenges, there are also opportunities for innovation and growth in the Andhra Pradesh agriculture sector. For example, the adoption of new technologies such as drones, machine learning, and IoT sensors can help farmers to make more informed decisions about planting, irrigation, and other key factors that affect crop yields.
By focusing on innovative solutions and investments, Andhra Pradesh’s agriculture sector can successfully navigate the challenges of the future and continue to provide food and livelihoods for millions of people in the region.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the history of soil formation in Andhra Pradesh?
The history of soil formation in Andhra Pradesh is a complex process influenced by geological factors such as parent material, climate, topography, vegetation, and time. These factors interact to create a variety of soil types over time.
2. How do soil types in Andhra Pradesh compare to soil types in other regions of India?
Soil types in Andhra Pradesh exhibit unique characteristics that influence soil fertility comparisons and crop suitability analysis. When compared to other regions in India, the differences in soil properties highlight the need for innovative approaches to optimize agricultural productivity.
3. What are the economic implications of Andhra Pradesh’s different soil types?
The economic implications of soil productivity in Andhra Pradesh are significant, as market demand for certain crops is affected by soil type. Understanding the relationship between soil fertility and crop yield is crucial for maximizing profitability and sustainability in agricultural production.
4. How have human activities impacted the quality of soils in Andhra Pradesh?
Soil degradation in Andhra Pradesh is a result of unsustainable agricultural practices. Overuse of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and irrigation has negatively impacted soil quality, leading to decreased crop yields and economic losses. Innovative solutions are needed to address this issue.
5. Are there any ongoing research projects related to soil management and agriculture in Andhra Pradesh?
Several ongoing research projects related to soil management and agricultural research are being conducted in Andhra Pradesh. These studies aim to improve soil health, increase crop productivity, and promote sustainable agricultural practices through innovative techniques and technologies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Andhra Pradesh has a diverse range of soil types that significantly impact its agriculture. The alluvial soils in the coastal regions are highly fertile and support the cultivation of various crops.
However, the black cotton soils in the Deccan plateau pose a challenge to farmers due to their high clay content, which makes them difficult to till.
The red soils, which are dominant in the Rayalaseema region, are also relatively infertile and require extensive fertilization.
Managing soil fertility is critical for sustainable agriculture in Andhra Pradesh. The state government has implemented various soil management practices such as soil testing, nutrient management, and crop rotation to improve soil health and increase crop yields.
However, the challenge of maintaining soil quality in the face of increasing population pressure and climate change remains a significant concern for the future of Andhra Pradesh’s agriculture.
In conclusion, the soil types of Andhra Pradesh are diverse and present unique opportunities and challenges for agriculture. Effective soil management practices and sustainable agriculture policies are critical to ensuring the long-term viability of the state’s agriculture.
As the state continues to grow and develop, it is essential to prioritize the conservation and improvement of its soil resources to support the livelihoods of its farmers and ensure food security for its population.
Learn more details about : Festivals Of Andhra Pradesh & Folk Dance Of Andhra Pradesh
- Sri Lalitha Ashtottara Shatanamavali in Telugu – శ్రీ లలితాష్టోత్తరశతనామావళిః - April 11, 2024
- Sri Durga Kavacham in Telugu – శ్రీ దుర్గా దేవి కవచం - April 10, 2024
- Shivananda Lahari in Telugu – శివానందలహరీ - April 9, 2024